My first experience in learning anything at all about color was in making color charts at the American Academy of Art. I was pretty bummed at the time and wanted to just move ahead to painting, but looking back now, it was a perfect introduction. In mixing up charts we learned about how paint handles, what happens when one color interacts with another, and how value is related to chroma. After this, we went on to painting monotone samples for a while, then with limited palettes, and finally full color, usually assignments ranging from still life painting, illustration, and figure painting. We always used gouache to paint, with the exception of specialized classes like oil painting or watercolor where we always painted from the model.
However, the real break through for me came from constant practice during my years as a background painter of environments and color scripts at Calabash Animation in Chicago combined with observational painting in my home studio and the Palette and Chisel Art League where Richard Schmid painted.
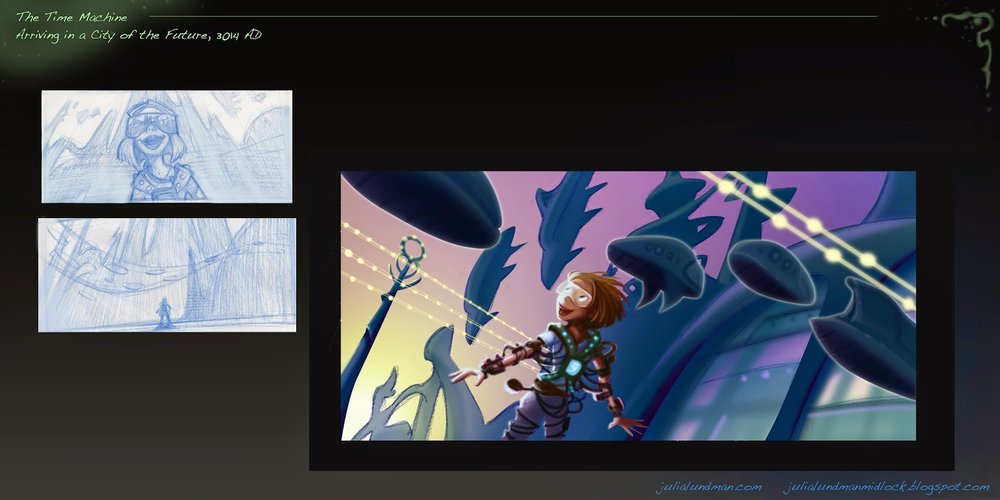
For my background painting job, there were usually 7-12 imaginary landscapes and interior paintings per commercial that I had to plan out and paint. Because of the fine art curriculum I took in art school, we rarely worked from imagination. My only guess then as to how to make convincing paintings with no reference was to apply the principles I learned about in Carlson's Guide to Landscape Painting, which I kept at my desk and referred to constantly. This forced upon me a need to truly understand the concepts of atmospheric perspective, the way color behaves while in a landscape, and other principles of lighting that cause changes on local color of objects. By working backwards, studying light and atmospheric perspective, I could then put those principles into practice on an imaginary stylized landscape.
A Lucky Charms commercial pan background I painted in gouache on illustration board, approximately 3 ft. x 14" wide, around 1994
However, just working from what I learned in Carlson's Guide to Landscape Painting was not enough. I also pored through books of other artists' work, studying paintings very, very closely. If I had no ideas on color schemes for seemingly mundane things like pavement or boring interior walls, I'd look at how Disney background painters were handling these subjects - usually with interesting lighting, chroma and contrast and learned how lighting and color can be an important compositional element in directing the eye. I combed through book stores and the library to find painters who were working from imagination; I practically memorized every inch of James Gurney's Dinotopia book for examples of great color.
"Lillies", 11x14, gouache on paper, 1992
But working from imagination alone, I believe, is not effective unless an artist works also from life. One tends to inform the other. During my years in Chicago, I regularly painted the still life, figures and portraits from life over at the Palette and Chisel, which helped me to develop a sense of how to mix paint, see color, simplify it, and apply it on canvas. I learned from Richard Schmid the principle of "cool light warm shadows, warm light cool shadows", something entirely new to me at the time. It was there that I learned how critical value relationships are to color, and how important it is to keep your color clean. Interestingly, I also learned from painting the figure and still life how it seems the majority of colors in any given subject seem to be more greyed down that I usually think at first, and how few really true high chroma colors are usually present.
Later on, when I needed to switch to painting in Photoshop at work, the Munsell Color System in the program gave me a way to visualize how connected the relationships are between hue, chroma, and value.
After having these experiences, I believe that learning about color is not simply the study of one component like a color wheel or color charts. I believe it has to be a combination of methods plus a relentless pursuit in training your mind to see and translate color accurately. I am still learning and sharpening my color and values sense, and hope that by making another concerted push now in my life I might break through a plateau I've been experiencing the past few years. By documenting my experiences and writing down what I know plus reading new research and methods while also painting from life, I hope to make some improvements.
********************************
Learning to Mix Color
Color mixing is one skill in a set of skills that an artist needs to develop for painting in color.
As stated earlier, the first time I ever mixed color was my first year in art school where we mixed color charts. Later, I made much more extensive charts on a recommendation that Richard Schmid made during a lecture at the Palette and Chisel. When he eventually wrote his book, Alla Prima, he included the exact same advice where you can find it to make your own charts.
The purpose of making color charts is not so that you have "recipes" for mixing color. These charts are not meant to be short cuts, recipes or formulas for color. At the time I made these I did not know what each oil color did when combined with another in the palette I was using. When I had problems remembering what, for instance, cadmium yellow deep did when combined with terra rosa, looking at these charts helped guide me. When I needed to figure out what color I was looking at in a still life, if I referred to these charts, it helped my eye understand what it was seeing in terms of chroma and value - usually I would mix that color up and go from there by adding a bit of a third.


Going through the process of mixing colors for charts like this is important in learning many useful things about how to handle paint, how to physically mix it, apply it, manipulate it into values, observe what happens to it's temperature, and notice how important it is to keep it clean. Making charts like this is also useful when you add a new color to your base palette or for experimenting with a set of colors to find how it reacts with other colors in your palette.
********************************
Learning to Identify Color
Sometimes while I was first learning to paint, I used a small piece of white paper with holes punched in it. I would look through this piece of paper when I was stuck, aligning it with the color I was trying to identify. Very often I was surprised at what I found - a color that was either more grey, less saturated, and not at all what I thought it was. Often, I would mix up what I was seeing through the hole and put a small swatch up on the white piece of paper. I would keep doing this until I got the correct color.
To help visualize what I mean, I made up an example from a recent photograph I took. Although the water is somewhat greenish blue, it can be very difficult to identify specifically. Here, by calling out swatches, you can see just how green the water is and what it's value is. Our minds might tell us that the mountains in the distance covered with pine trees must be green, also, however by calling out the swatch, we can see that the hills are not green, but greyed blues.

Since I was using Photoshop to make this example, I placed the color wheel there too so you can see where the green of the water is placed within that particular hue.
Isolating colors using a white card punched with a hole puncher can help break down the symbols of what our mind "thinks" it sees into what is actually there. Over time, this simple tool helped me to discover just how saturated or non-saturated a color might be.
********************************
Tools to Understand Color
After sifting through multiple websites, I finally found two excellent sites that explain color and how an artist uses it. Just about everything an artist needs to know about the physical properties of color and light can be found on these two sites.
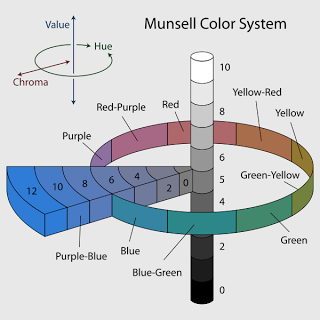
Other tools that help visualize and explain how color works are demonstrated in chart form. It is widely agreed within the realist painting community that the Munsell Color System is perhaps the most accurate way of understanding color and identifying it in context with other colors. The system identifies three terms: hue, chroma and value.